Air or Gas Temperature
The temperature of the air or gas stream plays a pivotal role in both the selection of pollution treatment technology and the efficiency of the adsorption process itself.
Adsorption relies on reducing the kinetic energy of pollutants. As temperature increases, gas molecules acquire higher kinetic energy, decreasing their residence time on the carbon surface and thereby diminishing adsorption efficiency.
Recommended Temperature Range:
Optimal adsorption occurs when the gas entering the system is below 40°C, and in some cases, even below 30°C, depending on the type of pollutants.
Temperature Effect on Adsorption:
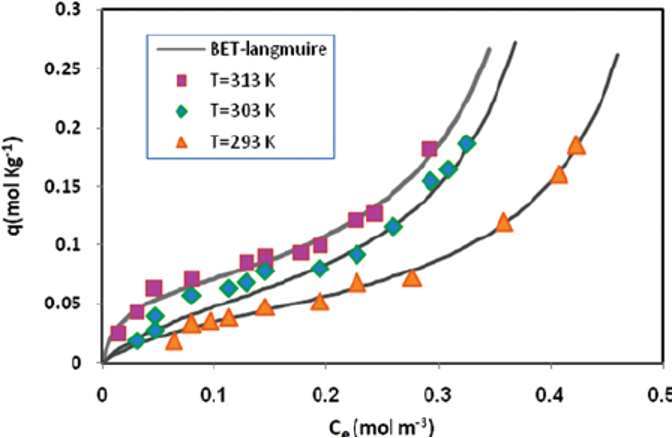
An adsorption isotherm graph illustrates the relationship between the concentration of pollutants on the carbon surface (q) and their concentration in the gas phase (Ce). At elevated temperatures, the adsorption capacity of the carbon significantly decreases; therefore, maintaining the lowest possible temperature during the process is essential.
Pressure
The pressure of gas streams directly affects the efficiency of pollutant adsorption onto activated carbon.
High Pressure:
Elevated pressure enhances the adsorption process by driving pollutant molecules deeper into the pores of the activated carbon, ensuring better utilization of the available surface area.
Low Pressure or Vacuum:
Under conditions of low pressure or vacuum, pollutant molecules tend to move away from the carbon, reducing process efficiency.
Despite the clear impact of pressure, in standard ventilation applications, its effect is less significant compared to temperature and humidity influences.
Humidity
Humidity is one of the most significant environmental factors affecting the adsorption efficiency of activated carbon. Relative humidity denotes the amount of water vapor present in the air or gas stream.
Adverse Effects of Humidity:
Competition with Pollutants:
Water vapor competes with pollutants for adsorption sites on the carbon substrate, leading to pore spaces being occupied by water instead of the desired pollutants.
Water Condensation:
Under conditions of low temperature or high water adsorption, water vapor can condense within the pores, obstructing pollutant access and impairing adsorption efficiency.
Recommended Humidity Levels:
- For optimal performance, it is advisable to maintain relative humidity below 50%.
- In high-humidity environments, such as those prevalent in Israel, effective adsorption can still be achieved at humidity levels of 65%-70%, depending on the application.
Pre-Treatment for High Humidity Streams:
In cases where relative humidity exceeds 70%, pre-treatment methods such as the use of air dryers, knockout drums (demisters), or coalescing vessels, are recommended before directing the gas into the carbon filter.
Interplay of Temperature and Humidity:
The relationship between temperature and humidity is intricate; thus, integrated management of both parameters is necessary to achieve optimal performance.
Environmental conditions are critical factors influencing the adsorption efficiency of activated carbon.
Designing systems with consideration of these factors can lead to significant performance improvements, reduced operational costs, and effective attainment of environmental objectives.
Summary
Environmental and Process Conditions – Temperature, Pressure, and Humidity – Are Critical Factors Affecting the Adsorption Efficiency of Activated Carbon. System design that accounts for these factors enables significant performance improvements, reduced operational costs, and optimal achievement of environmental objectives.
At Colligo-Tech, we specialize in tailoring activated carbon solutions to the unique needs of each client, employing cutting-edge technologies and in-depth knowledge of adsorption processes. Our expertise allows for performance maximization, compliance with environmental standards, and assurance of long-term system efficiency.
Interested in learning more? We are here to guide you every step of the way toward a customized solution!